This is your very first post. Click the Edit link to modify or delete it, or start a new post. If you like, use this post to tell readers why you started this blog and what you plan to do with it.


This is your very first post. Click the Edit link to modify or delete it, or start a new post. If you like, use this post to tell readers why you started this blog and what you plan to do with it.

There are three types of communication are the used for different purpose in data network.
-Unicast process of sending a packet from one host to an individual host.
-Multicast process of sending a packet from one host to all hosts in the network.
-Addresses process of sending a packet from one host to a selected group of hosts.
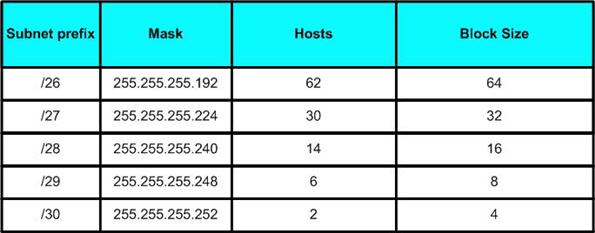
Subnetting is the practice of creating smaller network chunks that use a unique series of addresses, either to keep data inside the physical network or to funnel large numbers of addresses through a router or bridge to a single external Internet Protocol (IP) address.
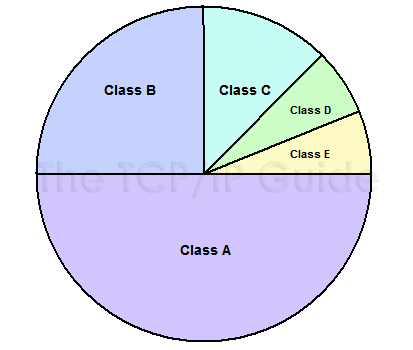
This topic talked about five in the “classful” system, which are given letters A through E. The first three, classes A, B and C, comprise most of the total address space (7/8ths of it). I’ve learned that classes A, B and C is the classes used for unicast IP addressing which means the message send to a single network, while class D is used for IP multicasting and class E was reserved for experimental use.
The MEDIUM provides the channel over which the message travels from source to destination.
Three types of media to interconnect devices and to provide the pathway over which data can be transmitted are:

Network Media
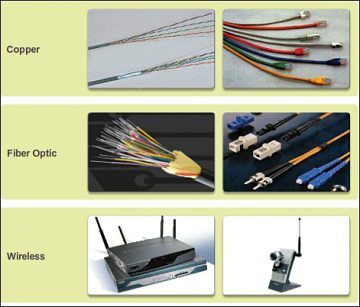
Network media is the actual path over which an electrical signal travels as it moves from one component to another. This chapter describes the common types of network media, including twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, fiber-optic cable, and wireless.
UTP cable
UTP Cable is a shorter way of saying unshielded twisted pair. This is one of the least expensive wires and works for basic needs of phone systems so it is one of the most commonly installed in residential industries.

STP cables are often used in Ethernet networks, particularly fast-data-rate Ethernets. The effectiveness of the additional covering varies according to the substance used for the shielding, such as:
It was originally designed by IBM for token ring networks that include two individual wires covered with a foil shielding, which prevents electromagnetic interference, thereby transporting data faster.

Coaxial Cable type of wire that consists of a center wire surrounded by insulation and then a grounded shield of braided wire. The shield minimizes electrical and radio frequency interference.

Fiber-optic cable is a networking medium capable of conducting modulated light trans-mission.
Wireless Communication
Wireless communication generally works through electromagnetic signals that are broadcast by an enabled device within the air, physical environment or atmosphere.
The sending device can be a sender or an intermediate device with the ability to propagate wireless signals. The communication between two devices occurs when the destination or receiving intermediate device captures these signals, creating a wireless communication bridge between the sender and receiver device.
Devices and media are the physical elements or hardware of the network.
PC, laptop, switch or cabling used to connect the devices.
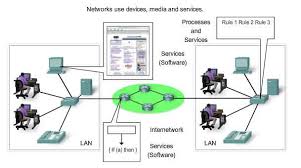
Services and processes are the communication programs, called software, that run on the networked devices.
END DEVICES AND THEIR ROLE IN THE NETWORK
END DEVICES these devices form the interface between the human network and the underlying communication network.
Examples of end devices are:
A host device is either the source or destination of a message transmitted over the network.
Servers are hosts that have software installed that enables them to provide information and services, like e-mail or web pages, to other hosts on the network.
INTERMEDIARY DEVICES AND THEIR ROLE IN THE NETWORK
Networks rely on INTERMEDIARY DEVICES to provide connectivity and to work behind the scenes to ensure that data flows across the network.
Examples of intermediary network devices are:
In this topic tackled about, Computer Network, Internetwork, How to get connected to the internet, why we need a computer network, network architecture, network basic and network cable. I learned that computer network is a set of connected computers. Computers on a network are called nodes. The connection between computers can be done via cabling, most commonly the Ethernet cable, or wireless through radio waves. Connected computers can share resources, like access to the Internet, printers, file servers, and others. A network is a multipurpose connection, which allows a single computer to do more. Computer network use standard Internet Protocol Suite to serve billions of users worldwide. Consists of million of private , public, academic, business and governments network, of local globe scope, that linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless and optical networking technologies. It is defined as a worldwide interconnection of computer that can share or exchange information to the users.
There are basic requirements to be connected to the internet a computer, a modem, a phone line, and a Internet Service Provider(ISP). We need a computer network help users on the network to share the resources and in communication. Can you imagine a world now without emails, online newspapers, blogs, chat and the other services offered by the internet?
File sharing networking of computers helps the network users to share data files.
Printer sharing is the process of allowing multiple computers and devices connected to the same network.
Communication and Collaboration is not easy for people to work together.
Organization, Remote Access, and Data protection. Device sharing is not possible

Network Architecture is the design of a communication network. It is a physical components and their functional organization and configuration, its operational principles and procedures, as well as data formats use.
Client/Server is type of networks that usually used in a corporate or in the business environment. Client a business user. Server is dedicated computer set up for more purposes . Peer-to-peer Architecture type of network usually find in home or in a small network, or less computers.
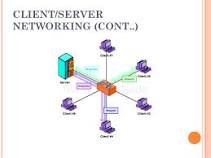
Networks Basic
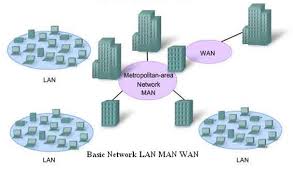
LAN is a group of computers and associated devices that share a common communications line or wireless link to a server. MAN is a computer network that interconnects users with computer resources in a geographic area or region larger. WAN computers connected to a wide-area network are often connected through public networks.